Kcynia
7
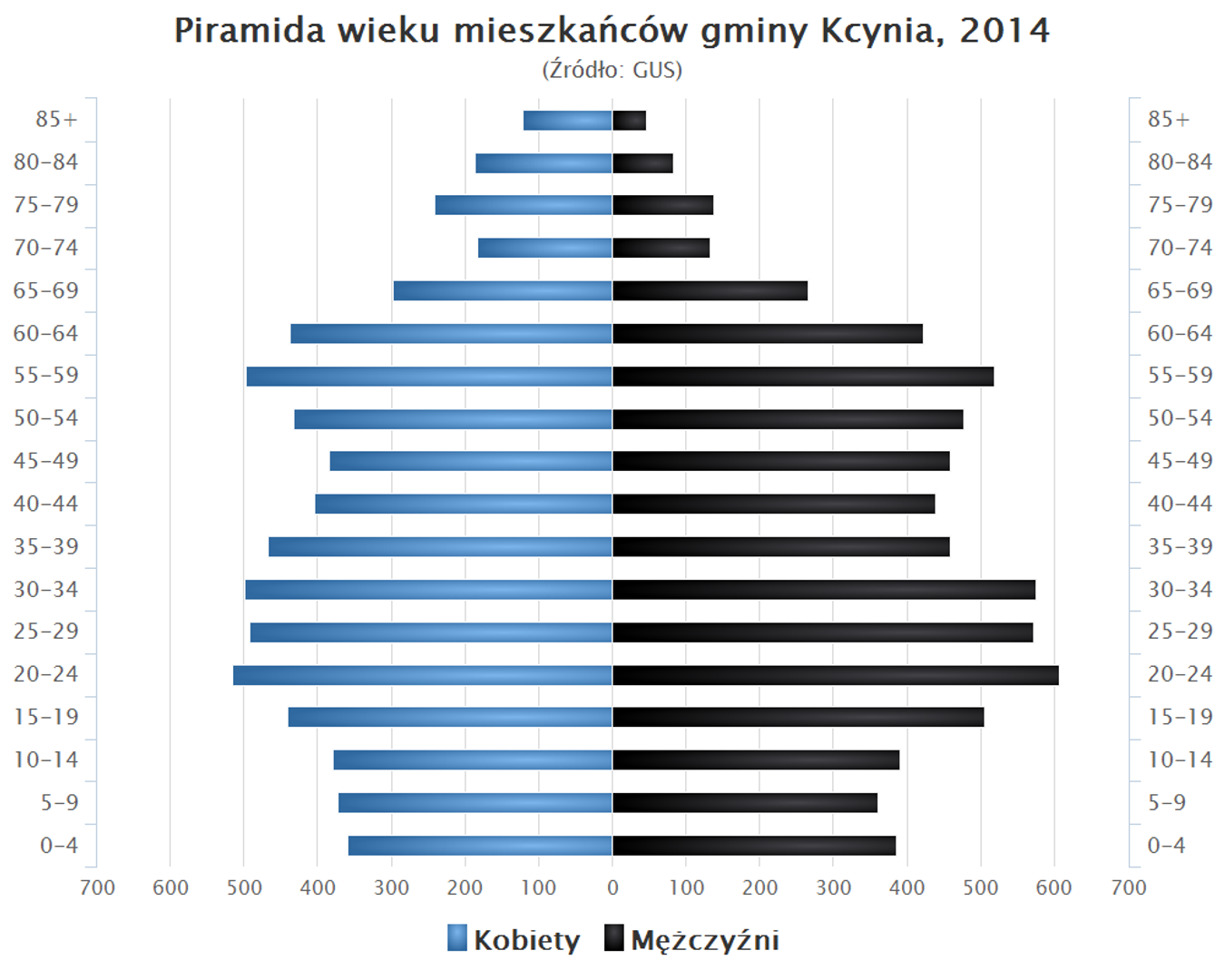
Overview
Kcynia is an urban-rural municipality in Poland, located in the Kuyavian-Pomeranian Voivodeship, within the Nakło County. Its history dates back to the years 1975–1998, when it was administratively part of the Bydgoszcz Voivodeship. The seat of the municipality is the town of Kcynia, which, according to data from 2004, had a population of 13,796. The municipality covers a significant area of 297.02 km², of which 71% is agricultural land and 20% is forest land, making it an important agricultural and forested region. An interesting natural feature is the Grocholin Nature Reserve, which protects a fragment of riparian forest. Kcynia is rich in architectural monuments, including many historic manor and palace complexes, dating mainly to the 19th and 17th centuries. The most important sites include the palaces in Chwaliszewo, Dobieszewo, Górki Dębskie, and Grocholin, as well as the Church of St. Michael the Archangel in Kcynia from 1631. Many of these monuments, such as the Carmelite monastery complex and the Roman Catholic cemetery, are protected as cultural heritage. The municipality also has an attractive administrative structure, encompassing numerous villages and localities, which contributes to local integration and cooperation. Interestingly, Kcynia is a member of the Association of Polish Small Towns (Unia Miasteczek Polskich), highlighting its role in regional development and the promotion of local culture. The municipality borders other municipalities, such as Gołańcz, Nakło nad Notecią, and Szubin, fostering local cooperation.
Location
You can also find here:
2026 Wizytor | All Rights Reserved
